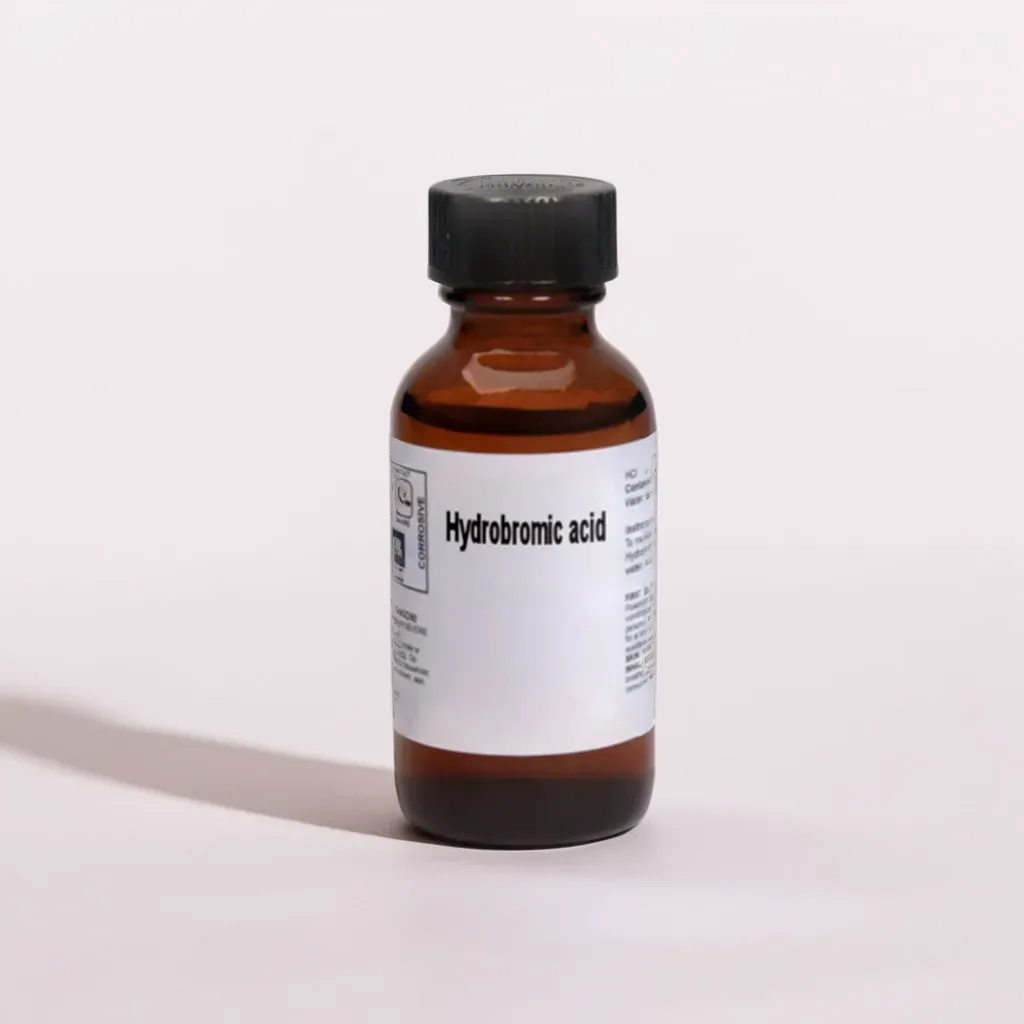
Hydrobromic-Acid
Description
Hydrobromic acid, a strong acid formed by dissolving hydrogen bromide (HBr) in water, is known for its significant role in chemical synthesis and industrial applications.
It serves as a reagent in the production of bromine compounds, an essential process in organic chemistry. Its potent properties also make it valuable in the pharmaceutical industry for manufacturing various drugs.
Hydrobromic acid’s efficiency in dissolving metals and its use in refining processes further underscore its importance in scientific and industrial settings.
- Product name : Hydro bromic Acid
- Cas No : 10035-10-6
- Molecular Formula : HBr
- Molar Mass : 80.9119 g/mol
- Melting Point : - 11 °C (47-49% w/w aq.)
- Boiling Point : 122 °C at 700 mmHg (47-49% w/w aq.)
- Synonyms : Hydrogen bromide

PRODUCT NAME: HYDROBOMIC ACID 48%
SR NO | TEST | RESULT |
1 | DESCRIPTION | COLOURLESS |
2 | ASSAY | 48.2% |
3 | SP.GRAVITY | 1.49 gm./ml |
4 | BOILING POINT | 122.2 Degree |
5 | CHLORIDE | NOT DETECTED |
6 | SULPHATE | 0.01% |
7 | FREE BROMINE | NOT DETECTED |
Packaging:
Hydro bromic acid is supplied in the following packaging:
- Drums
- Intermediate Bulk Containers – IBCs
- Bulk Truck Loads
Flammability and Exclusivity
Hydro bromic acid is non-flammable and non-explosive. At high temperature it will release toxic fumes of hydrogen bromide.
Toxicity
LD50 (inhalation rate): HBr 100% 2,858 ppm/1h. Hydro bromic acid is corrosive to eyes, skin and mucous membranes. Actual inhalation may produce delayed pulmonary edema. Direct contact results in serious corneal and skin burns.

Packaging:
Hydro bromic acid is supplied in the following packaging:
- Drums
- Intermediate Bulk Containers – IBCs
- Bulk Truck Loads
Flammability and Exclusivity
Hydro bromic acid is non-flammable and non-explosive. At high temperature it will release toxic fumes of hydrogen bromide.
Toxicity
LD50 (inhalation rate): HBr 100% 2,858 ppm/1h. Hydro bromic acid is corrosive to eyes, skin and mucous membranes. Actual inhalation may produce delayed pulmonary edema. Direct contact results in serious corneal and skin burns.

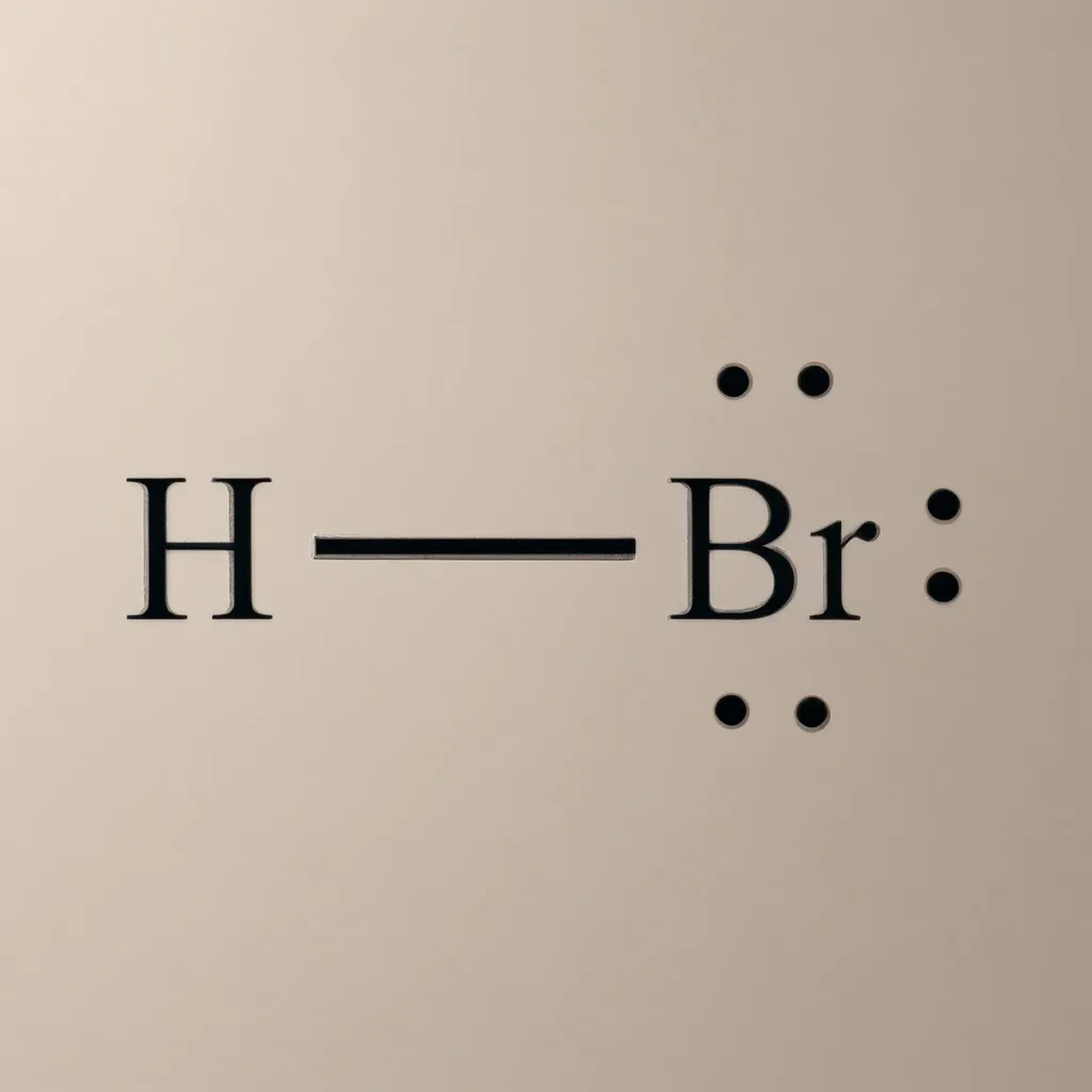
Uses of Hydro bromic Acid
- Hydrobromic acid is utilised in the production of inorganic and organic bromine compounds, crucial for various industrial applications.
- It plays a significant role in the pharmaceutical industry, aiding in the synthesis of bromine-containing medications.
- This acid is effective in metal refining and recovery processes due to its strong reactivity with metals.
- Additionally, hydrobromic acid is used in laboratory research as a reagent for chemical reactions requiring a strong acid.
Storage & Handling:
When handling and storing hydrobromic acid, it’s crucial to use containers resistant to strong acids and ensure they are tightly sealed to prevent leaks and evaporation. Store in a cool, well-ventilated area away from incompatible materials like bases and oxidising agents.
Personal protective equipment, including gloves and eye protection, should always be worn to avoid direct contact with the skin or eyes, and to protect from potentially harmful fumes. Safety showers and eyewash stations should be accessible in areas where the acid is handled.

